El Niño is the warm phase of the El Niño La Niña Southern Oscillation (ENSO), which occurs about every five years in the tropical Pacific Ocean. ENSO affects weather systems around the world, bringing extremes such as floods and droughts. El Niño typically makes Australia and Southeast Asia drier, while the Americas are wetter and warmer.
Juan Gaertner/Science Photo Library | Science Photo Library | Getty Images
A climate pattern known as El Niño has arrived and is expected to become more intense in winter, with the potential to bring warmer temperatures and more extreme weather conditions, According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
“The El Niño phenomenon is in place and is expected to gradually intensify into the northern hemisphere winter,” NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center said in a report. Advisory issued on Thursday.
El Niño (“little boy” in Spanish) and La Niña (“little girl” in Spanish) are weather patterns in the Pacific Ocean that Affects weather conditions around the world.
In the U.S., a moderate-to-severe El Niño in fall and winter is associated with above-average humidity from southern California to the Gulf Coast and above-average dryness in the Pacific Northwest and Ohio Valley, NOAA said. related to level.It also increases the likelihood of warmer-than-average winters in the northern U.S.
“We’ve been anticipating this for months, and we’re still waiting to see how big this is going to be,” he said. Gavin A. SchmidtThe director of NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies told CNBC. According to NOAA, the first advisory observation for El Niño was issued on April 13.
“El Niño tends to peak around December/January, it can be a small event, it can be a large event, and the impact we’ll see will depend on that,” Schmidt told CNBC.
NOAA said there was an 84 percent chance of a stronger than moderate El Niño and a 56 percent chance of a strong El Niño by winter.
Globally, “we’re going to see more drought and fires in Indonesia/Australia and more flood damage/extreme rainfall in eastern South America,” Schmidt said.
Areas likely to experience high temperatures range from the Tropic of Cancer to 60 degrees north of the equator, including much of the United States and Eurasia, Schmidt said. While temperatures are likely to rise in these regions, Schmidt is careful to note that an El Niño does not guarantee that any region will record high temperatures.
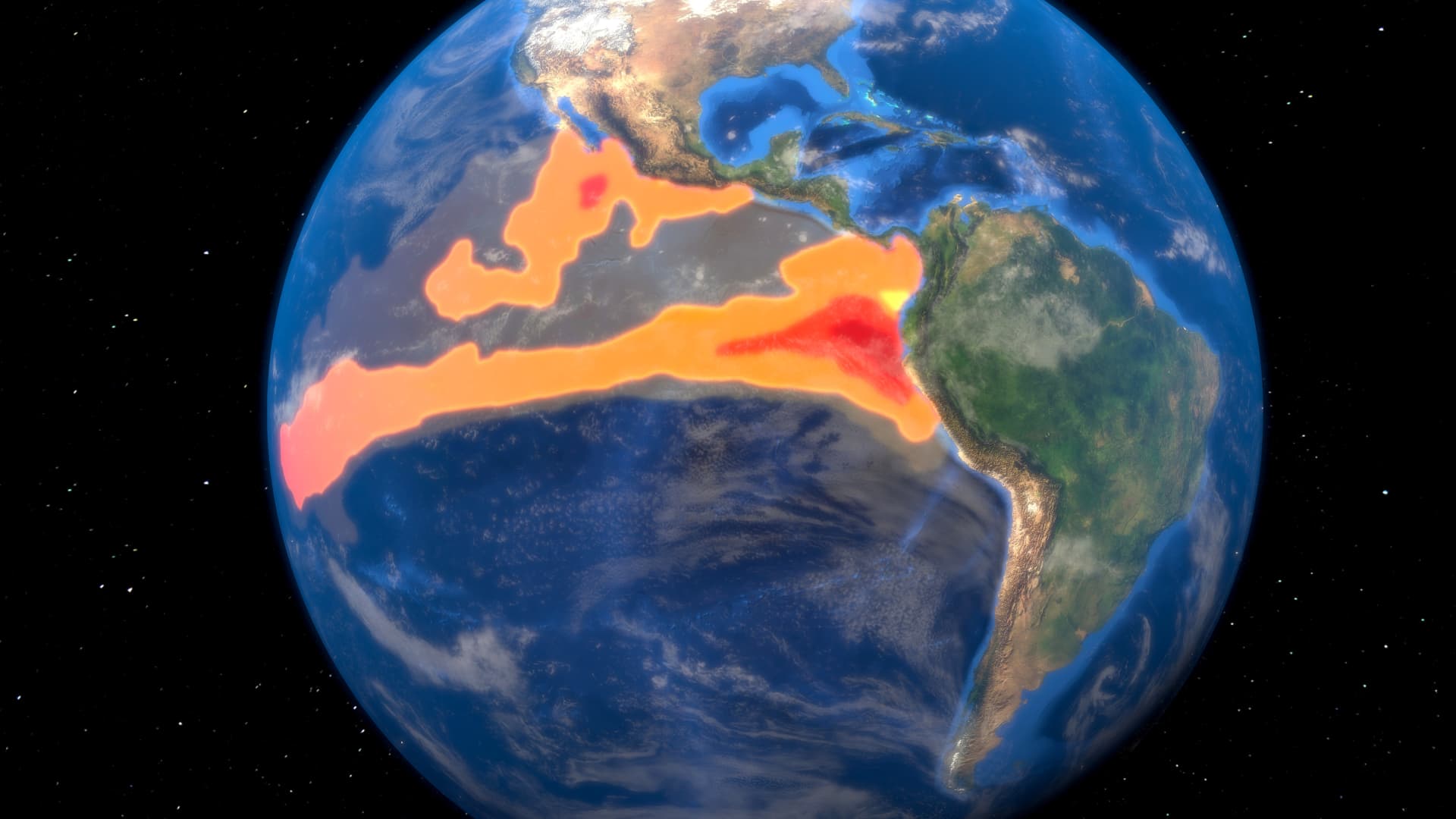
Animation of sea surface temperature over the past 6 months
NOAA
El Niño could give average global temperatures a “boost” in 2024, but probably not enough to raise average global temperatures by more than 1.5 degrees Celsius, Schmidt said.
How climate change affects El Niño is “still unclear,” Schmidt said.
While the exact link between climate change and El Niño is unclear, Schmidt said, El Niño does exacerbate conditions already created by climate change on a regional scale.
normal weather pattern Trade winds blow westward along the equator. In an El Niño weather pattern, the trade winds weaken and warmer waters are pushed eastward, the west coast of the Americas.Warmer waters move the Pacific Ocean jet stream, which is a stream of air that flows around the earth from west to east, heading south, making northern parts of the U.S. and Canada drier and warmer than usual. In states along the U.S. Gulf Coast, this change in weather patterns has resulted in wetter weather, which tends to see more flooding in the region, according to NOAA.
During La Niña, trade winds are stronger than usual and more warm water is being pushed into Asia. That pushed the jet stream northward, causing drought in the southern United States, heavy rain and flooding in the Pacific Northwest and Canada, According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.